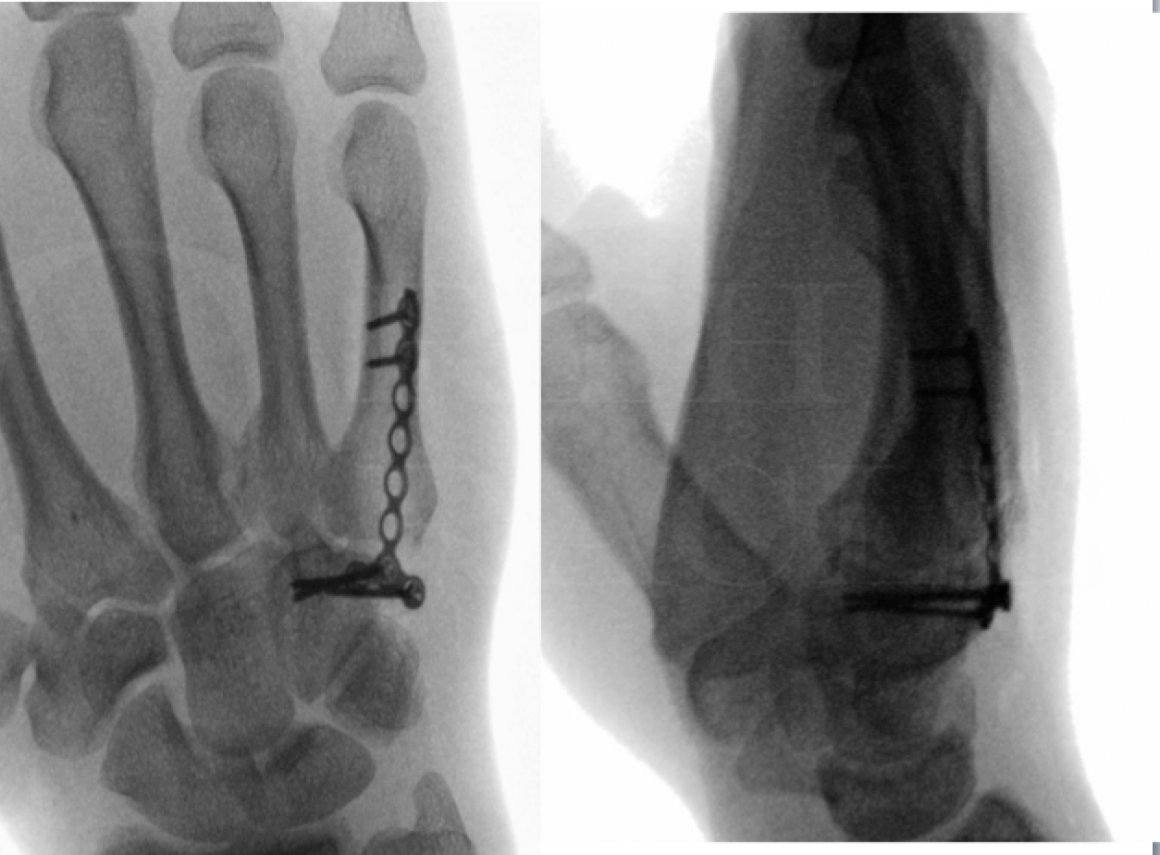
Case Report in Military Hospital 175
 Loading…
Loading…
Current Concepts in 3D Assisted Corrective Operations
Three-dimensional (3D) planning and printing have significantly impacted the field of orthopedics, particularly in the management of distal radius fractures and malunions. The integration of computer-assisted technologies in preoperative planning has enhanced the visualization of fractures and surgical plans (Yoshii et al., 2021). This advancement has resulted in improved accuracy in preoperative planning for osteosynthesis procedures, leading to better outcomes for patients undergoing surgical treatment for distal radius fractures (Katt et al., 2020).



The use of 3D modeling and computer-generated osteotomy guides has been recognized as a promising approach for addressing distal radius malunions (Katt et al., 2020). These technologies provide a more precise and tailored method for surgical treatment, potentially improving postoperative results. Additionally, the application of three-dimensional (3D) computer-assisted plans with custom-made cutting jigs has been identified as a best practice in preoperative planning for distal radius fracture malunions (Evans & Jupiter, 2019).
Virtual planning of corrective osteotomies for distal radius malunions has demonstrated high accuracy and is preferred over traditional planning on physical models (Stockmans et al., 2013). The integration of three-dimensional computer simulation and patient-specific guides in corrective osteotomies for distal radius malunions has shown promising results in achieving anatomical reduction and enhancing functional outcomes for patients (Michielsen et al., 2018). This approach allows for detailed preoperative planning and precise execution of surgical techniques, ultimately improving patient care.

In the future, the use of three-dimensional custom guides in corrective osteotomies for distal radius malunions is expected to further enhance the precision and effectiveness of surgical interventions in orthopedics (Daoulas et al., 2023). By leveraging advanced technologies such as 3D planning and printing, orthopedic surgeons can continue to enhance patient outcomes, reduce surgical complications, and optimize the overall quality of care in the management of distal radius fractures and malunions.
References
- [1] (2021). Three-dimensional evaluations of preoperative planning reproducibility for the osteosynthesis of distal radius fractures. journal of orthopaedic surgery and research, 16(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-021-02278-9
- [2] (2020). Distal radius malunion. the journal of hand surgery, 45(5), 433-442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhsa.2020.02.008
- [3] (2019). Best approaches in distal radius fracture malunions. current reviews in musculoskeletal medicine, 12(2), 198-203. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12178-019-09540-y
- [4] (2013). Accuracy of 3d virtual planning of corrective osteotomies of the distal radius. journal of wrist surgery, 02(04), 306-314. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0033-1359307
- [5] (2018). Corrective osteotomy of distal radius malunions using three-dimensional computer simulation and patient-specific guides to achieve anatomic reduction. european journal of orthopaedic surgery & traumatology, 28(8), 1531-1535. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-018-2265-0
- [6] (2023). Corrective osteotomy of a distal radius malunion using three-dimensional custom guides. annals of 3d printed medicine, 9, 100099. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stlm.2023.100099